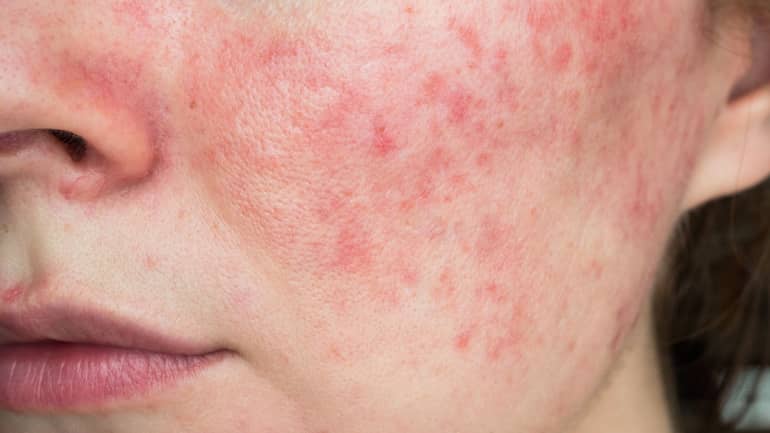
Acne can appear in areas where sebaceous glands are most numerous, most commonly on the face, but can occur on the back, shoulders, chest and neck. Acne can occur in the form of comedones, papules, pustules, small nodules and inflamed cysts.
Comedones are non-inflammatory skin changes resulting from the blockage of sebaceous glands, sometimes also called white pimples or blackheads. Papules, pustules, nodes and cysts are inflammatory changes in the skin. They result from bacterial development. One type of bacteria plays an important role in the development of these inflammatory changes and it is called Propyonbacterium acne.
Acne can be caused by a number of factors: hormonal changes (especially during puberty and menstrual cycles), stress, hyperactivity of the sebaceous glands and accumulation of dead skin cells, bacteria, skin irritation, anabolic steroids.

There are several forms of acne, the most common is acne vulgaris, which primarily occurs in adolescents in whom hormonal changes cause an increase of sebaceous glands and the creation of sebum.
Almost every person aged 12-17 has acne (they occur in 80-85% of adolescents). These changes usually completely diminish after the age of 20, but they can last till the age of 30 or even 40, particularly in women (up to 7% of the population in these age groups has some form of acne).
Treatment of acne depends on the degree of acne and the severity of skin changes. In milder forms the therapy is applied locally. In moderate to severe forms, systemic therapy supplements local therapy.
There are five groups of drugs used to treat acne, and each group has different mechanisms of action: local antibiotics and antiseptics, drugs that interfere with keratinisation, oral antibiotics, contraceptives and vitamin A analogues.
In the mild forms of acne, treatment starts with proper skin care and cleaning with a mild cleaning agent. In addition to this, antibiotics (clindamycin, erythromycin), antiseptics (benzoyl peroxide, aselaic acid) and drugs that prevent keratinisation (adapalene, tazarotene, tretinoin) are used. These drugs can be used alone but provide better results when combined. Cleaning the skin and applying local therapy can remove excess oil and promote skin peeling. This prevents clogging of the follicle openings and the creation of new whiteheads, papules and pustules.
Results of the local acne treatment are visible only after 6-8 weeks. In the event that local therapy does not yield satisfactory results, oral antibiotics can be used. Antibiotics should be taken for a longer period of time, usually for several months. In addition to antibiotics, local treatment is usually carried out. In females with a severe form of acne that does not respond to oral antibiotics and topical therapy, treatment with oral contraceptives should be considered too.
In severe forms of acne the analogue of vitamin A (isotretinoin) is applied, which is very effective, but because of possible side effects, this treatment should be conducted under medical supervision. Caution is needed especially in female patients, because these drugs are strictly prohibited during pregnancy.