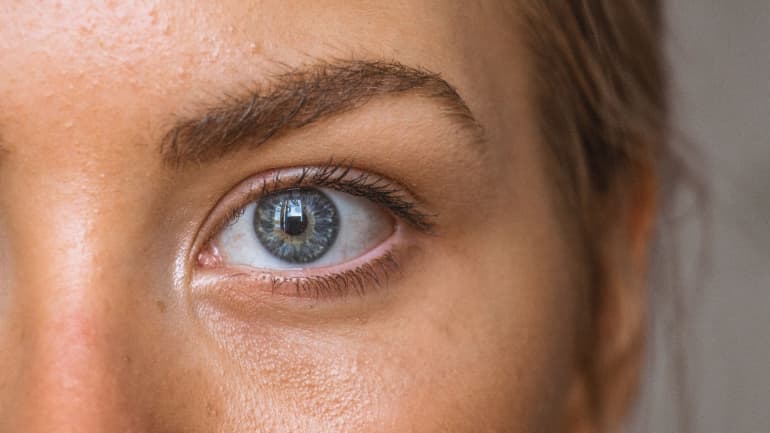
Over time, the redness progresses, i.e. blood vessel dilation occurs (teleangiectasia). In the worst cases, infiltration and proliferation of connective tissue of the skin is present. This leads to aggravation of the symptoms and changes on the nose, a condition called rhinophyma.
It is estimated that this disease affects 0.5% to 10% of the population. It is more common in people with a fair complexion and light eyes.
The real cause of the disease has not yet been found, but it is a combination of environmental and genetic factors. The disease typically occurs after the age of thirty and is somewhat more common in women. Patients with rosacea complain of occasional redness on the face that is usually associated with some provoking factors.
There are various provoking factors associated with redness and disease progression: warm weather, exercise, very spicy food, cold weather, warm bath, wind, alcohol, emotional stress, sun exposure, skin care products, hot drinks.
At the beginning of the disease the occurrence of redness is temporary and solely related to provoking factors. The disease progression increases the facial redness even more and it is accompanied by tingling and burning in the face. Redness in the face becomes permanent. The dilation of blood vessels (telangiectasia) and the swelling of face, which may become permanent, also appears. Eye symptoms, such as burning and itching eyes, and the red sclera can also develop. With further disease progression and the development of inflammatory changes, facial skin looks like a case of severe forms of acne. Proliferation of connective tissue leads to an increase and changes of the nose. This change of the nose is called rhinophyma.
Rosacea is not a serious disease, but it has a significant impact on quality of life.

It can be confused with other skin diseases such as acne, contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, steroid rosacea, etc. It is very important to diagnose the disease on time and implement an appropriate therapy to prevent the disease progression to severe clinical forms.
Treatment of rosacea is symptomatic and depends on the severity of the disease. Above all, it is necessary to avoid any provoking factors which give rise to redness “attacks”. Attention should be paid to the use of hypoallergenic and non-irritating facial cosmetics.
Those most commonly applied are topical drugs which have a symptomatic effect on redness and inflammation, like local antibiotics (metronidazole) and aselaic acid. The treatment is carried out for several months, and when an appropriate clinical response is reached, further treatment is adjusted to the disease progression. Sometimes it is necessary to conduct a systemic treatment with antibiotics (doxycycline, tetracycline).
Despite the fact that rosacea is a chronic disease that progresses gradually, the final outcome of the disease greatly depends on the patient’s behaviour and compliance with recommendations for treatment.