Changes occur in the so-called seborrheic areas where sebaceous glands are most numerous. The occurrence of seborrhoea is primarily influenced by hereditary factors, then hormonal and above all emotional factors (stress) and individual nutritional factors (alcoholic drinks, spicy foods, etc.).
Increased secretion of sebum is also stimulated by some drugs such as corticosteroids, synthetic gestagen and tranquilizers, and it was also observed in patients with, for example, Parkinson’s disease. Seborrhoea is also a significant predisposing factor for the development of seborrheic dermatitis, acne vulgaris, rosacea and gram-negative folliculitis.
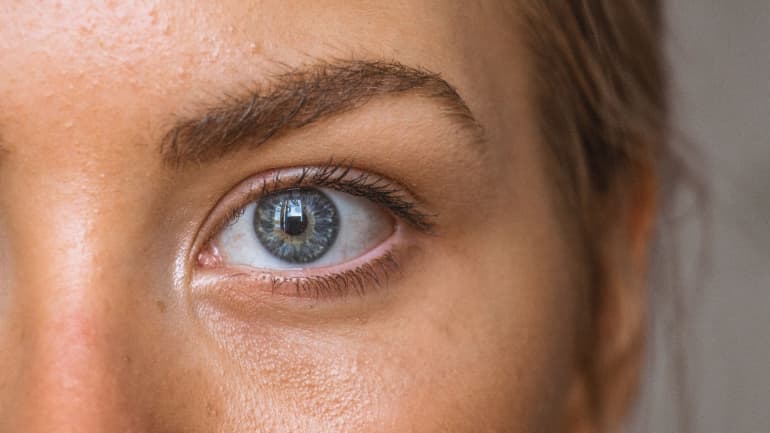
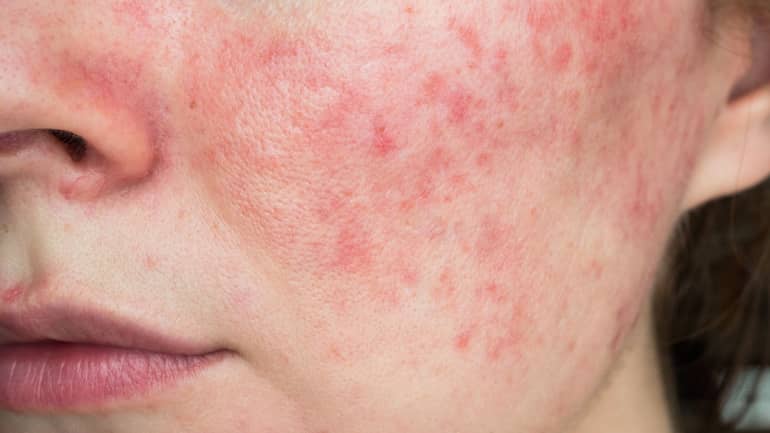
Clinically, in the seborrheic areas, the skin is oily, shiny, the follicle openings are expanded, and due to the clogging of follicles, numerous comedones are observed on the skin of the face. Hair quickly becomes oily, and changes are often accompanied by scalp scaling. If the seborrheic areas develop an inflammation, this is called seborrheic dermatitis.
For treatment, it is recommended to use shampoos containing sulphur, selenium sulphide, zinc pyrithione or tar or magistral alcohol preparations with sulphur, salicylic acid and resorcinol. Changes are chronic, and in the summer they are a bigger problem, partly because they are accompanied by increased sweating.